![]()
Auden Park Family Dentistry Your Dentist in Kingston, ON
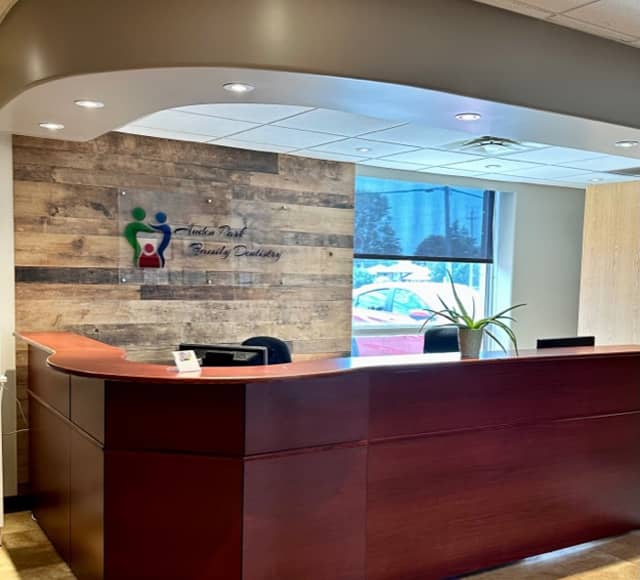
Welcome to Auden Park Family Dentistry! We love what we do, and we treat our patients as part of our family. We take the time to get to know each of our patients and understand their personal dental needs. Whether you are a senior or would like to bring your child for their first dental visit, we look forward to meeting with you and being a part of your unique oral health journey.
Our dentist in Kingston, ON, has provided high-quality dental care to the families of Kingston, Ontario, for over 20 years through the Canadian Dental Care Plan.
Our dentists near you are dedicated to your oral health and overall well-being by creating a relaxed and comfortable environment. If you need us, we are just a phone call away at (613) 389-0538, We try to accommodate same-day dental emergency appointments.


Full-Service Dental Clinic
At Auden Park Family Dentistry, we offer a wide range of general, cosmetic, restorative and orthodontic dental treatments to our patients of all ages. Our dental office in Kingston understands the convenience and reliability that come with receiving all of our dental care needs in one place.
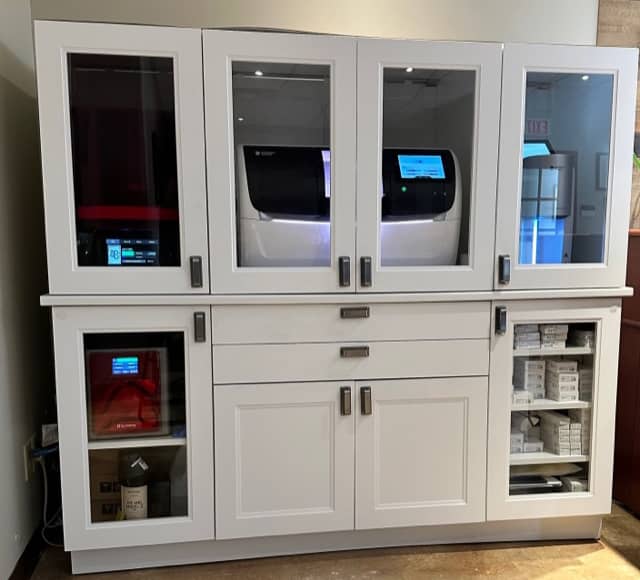
Advanced Technology
One of our highest priorities is providing our patients with the highest quality dental care, and part of this is having access to advanced technology within the practice. Our team utilizes dental technology and equipment that promotes quality dental care and treatment.

Same-Day Dental Emergencies
When it comes to dental emergencies, urgency is key. If you or your family members are experiencing a facial injury that has resulting in a knocked out, broken, chipped or infected tooth, we have got you covered! Contact us to receive immediate treatment.

Personalized Dental Care
Auden Park Family Dentistry is a family-owned clinic that treats our patients as part of our family. Our dentist near you provides a relaxing and comfortable environment. Our team values getting to know each of our patients and treating their individual dental needs.
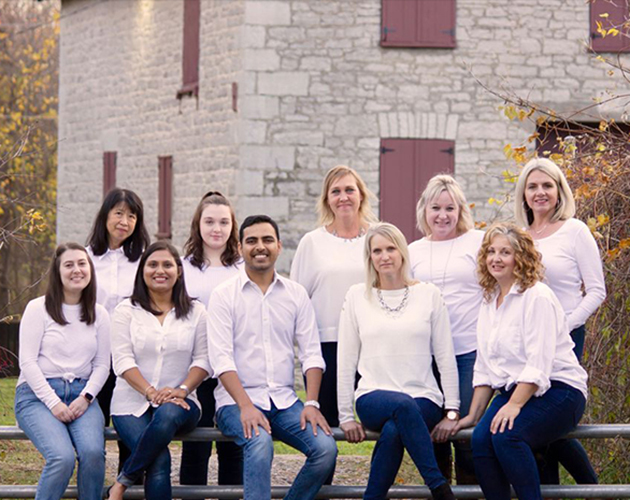

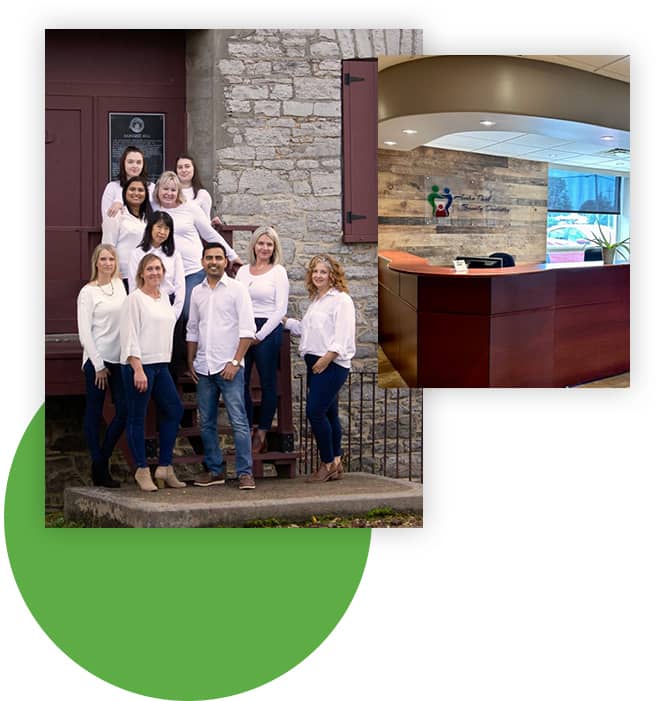
Meet Our Dedicated Kingston Dentists
Auden Park Family Dentistry is a general and cosmetic family dental office that caters to patients of all ages. We believe everyone deserves to have a smile that’s healthy and beautiful. Our practice is proud to offer a wide range of dental services to our patients in Kingston, Amherstview and surrounding communities. The caring and skilled dental team at Auden Park Family Dentistry strives to accommodate each and every patient that come to see us. We are always available to answer any questions you may have, in-office, or over the phone. Our Kingston dentists is experienced and will go above and beyond to ensure that each patient feels comfortable and welcome while receiving dental care.

Dental Care for the Whole Family in Kingston
Auden Park Family Dentistry goes above and beyond to provide patients with a comfortable and reliable space to receive dental care. We take the time to educate our patients regarding their recommended treatment process and help prioritize their oral health and overall wellness. Our dentist in Kingston utilizes advanced dental technology to ensure your treatment process is both efficient and effective. We also take same-day emergency dental cases, so please do not hesitate to visit us.
Our Kingston Dental Clinic Gallery

Meet Our Kingston Dental Team
Their skills and experience are in service of the beauty and health of your smile.
Our Dental Office Services in Kingston
Dental Cleanings & Check-Ups
Regular dental cleanings and check-ups are essential to maintaining good oral health and preventing dental problems.
Mouth & Sports Guards
Mouthguards and sports guards are protective devices designed to cover and cushion the teeth, gums, during physical activities or while you sleep.
Dental Implant Treatment
Dental implants are considered a permanent and durable solution for tooth replacement.

Wisdom Tooth Extractions
Wisdom tooth extraction is a common dental procedure in which one or more of the third molars, commonly known as wisdom teeth, are removed.
Sedation Dentistry
Sedation dentistry is a dental practice that involves the use of sedative medications to help patients relax and remain calm during dental procedures.
Teeth Whitening Treatment
Teeth whitening is a cosmetic dental procedure aimed at lightening the color of the teeth and removing stains or discoloration.
















